Scatter Plots |
2025-07-14 |
Scatter plots represent the relationship between two different numeric measurements. Each dot is positioned based on the value of the values selected for the X and Y axes.

 There are four tabs:
There are four tabs:
 For this example, we've removed the color and shape columns to make it easier to see the two axes in the plot. Click Apply.
For this example, we've removed the color and shape columns to make it easier to see the two axes in the plot. Click Apply.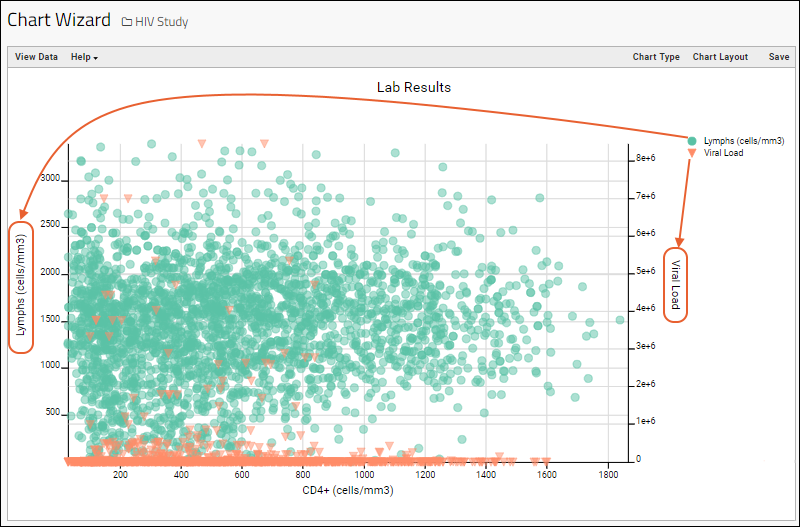 If you use the Chart View > Number of Charts > One Per Measure, you will see two separate charts, still respecting the Y Axis sides you set.
If you use the Chart View > Number of Charts > One Per Measure, you will see two separate charts, still respecting the Y Axis sides you set.
 Once you have saved a scatter plot, it will appear in the Data Browser and on the (charts) menu for the source dataset. You can manage metadata about it as described in Manage Data Views.
Once you have saved a scatter plot, it will appear in the Data Browser and on the (charts) menu for the source dataset. You can manage metadata about it as described in Manage Data Views.
 Export your completed chart by clicking an option:
Export your completed chart by clicking an option:
Create a Scatter Plot
- Navigate to the data grid you want to visualize.
- Select (Charts) > Create Chart. Click Scatter.
- The columns eligible for charting from your current grid view are listed.
- If you want to plot using a column that is not visible here, return to the data grid and use (Grid Views) > Customize Grid to add it.
- If your server is configured to restrict charting to columns marked as "measures" or "dimensions", you will only be able to use columns with those designations.
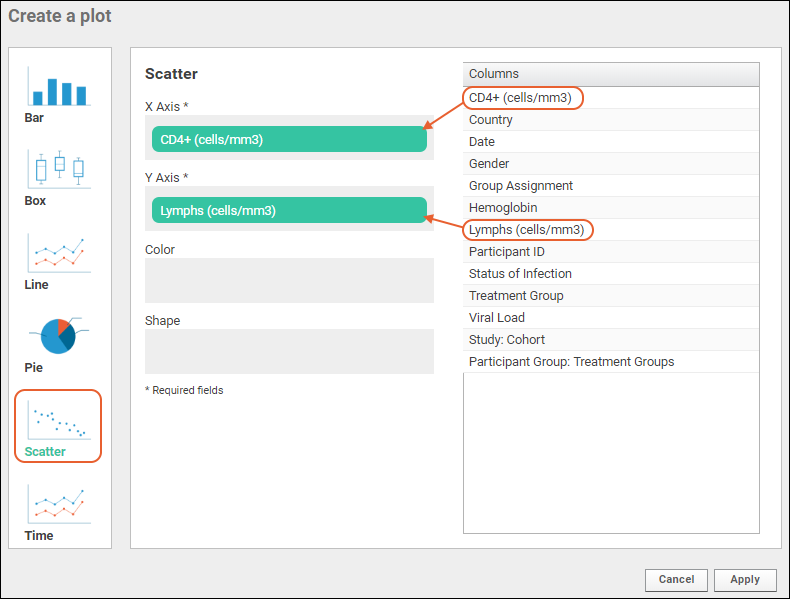
- Select the X Axis column by drag and drop.
- Select the Y Axis column by drag and drop.

- Only the X and Y Axes are required to create a basic scatter plot. Other options will be explored below.
- Click Apply to see the basic plot.
- Click View Data to see, filter, or export the underlying data.
- Click View Chart to return. If you applied any filters, you would see them immediately reflected in the plot.
- Customize your visualization using the Chart Type and Chart Layout links in the upper right.
- Chart Type reopens the creation dialog allowing you to:
- Change the X or Y Axis column (hover and click the X to delete the current selection).
- Add a second Y Axis column (see below) to show more data.
- Optionally select columns for grouping of points by color or shape.
- Note that you can also click another chart type on the left to switch how you visualize the data with the same axes and color/shape groupings when practical.
- Click Apply to update the chart with the selected changes.
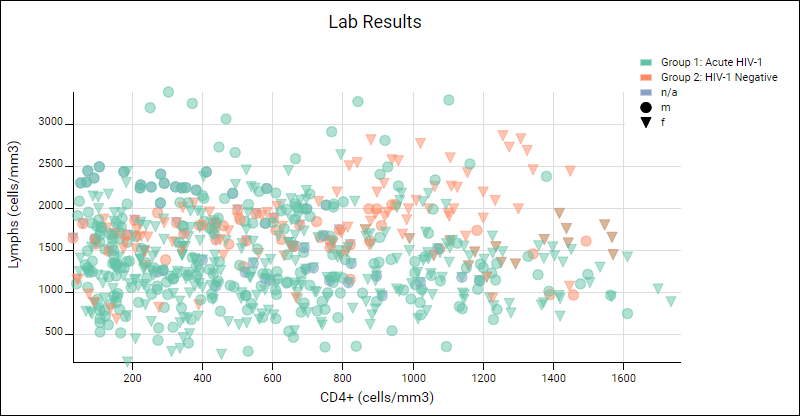
- Here we see the same scatter plot data, with colors varying by cohort and points shaped based on treatment group. Notice the key in the upper right.
Change Layout
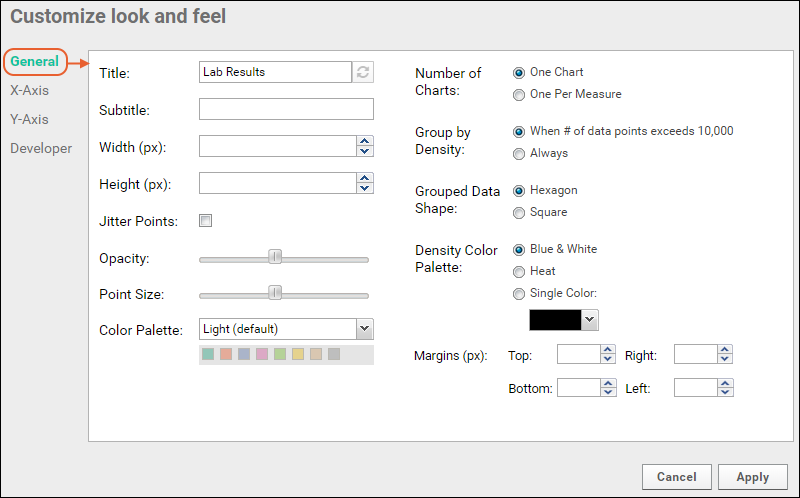
The Chart Layout button offers the ability to change the look and feel of your chart.- General:
- Provide a title to display on the plot. The default is the name of the source data grid.
- Provide a subtitle to display under the title.
- Specify a width and height.
- Choose whether to jitter points.
- Control the point size and opacity, as well as choose the default color palette. Options: Light (default), Dark, and Alternate. The array of colors is shown under the selection.
- Number of Charts: Select either "One Chart" or "One Per Measure".
- Group By Density: Select either "Always" or "When number of data points exceeds 10,000."
- Grouped Data Shape: Choose either hexagons or squares.
- Density Color Palette: Options are blue & white, heat (yellow/orange/red), or select a single color from the dropdown to show in graded levels. These palettes override the default color palette and other point options in the left column.
- Margins (px): If the default chart margins cause axis labels to overlap, or you want to adjust them for other reasons, you can specify them explicitly in pixels. Specify any one or all of the top, bottom, left, and right margins. See an example here.
- X-Axis/Y-Axis:
- Label: Change the display labels for the axis (notice this does not change which column provides the data). Click the icon to restore the original label based on the column name.
- Scale Type: Choose log or linear scale for each axis.
- Range: Let the range be determined automatically or specify a manual range (min/max values) for each axis.
- Developer: Only available to users that have the "Platform Developers" site role.
- A developer can provide a JavaScript function that will be called when a data point in the chart is clicked.
- Provide Source and click Enable to enable it.
- Click the Help tab for more information on the parameters available to such a function.
- Learn more in this topic.
Add Second Y Axis
You can add more data to a scatter plot by selecting a second Y axis column. Reopen a chart for editing, click Chart Type, then drag another column to the Y Axis field. The two selected fields will both have panels. On each you can select the side for the Y Axis using the arrow icons.Example: Heat Map
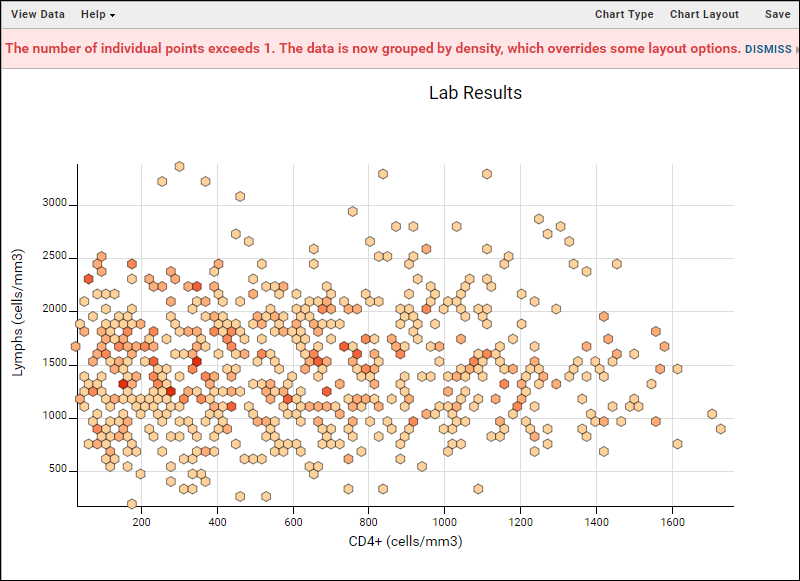
Displaying a scatter plot as a heatmap is done by changing the layout of a chart. Very large datasets are easier to interpret as heatmaps, grouped by density (also known as point binning).- Click Chart Layout and change Group By Density to "Always".
- Select Heat as the Density Color Palette and leave the default Hexagon shape selected
- Click Apply to update the chart with the selected changes. Shown here, the number of charts was reset to one, and only a single Y axis is included.
- Notice that when binning is active, a warning message will appear reading: "The number of individual points exceeds XX. The data is now grouped by density which overrides some layout options." XX will be either 10,000 or 1, if you selected "Always" as we did. Click Dismiss to remove that message from the plot display.
Save and Export Plots
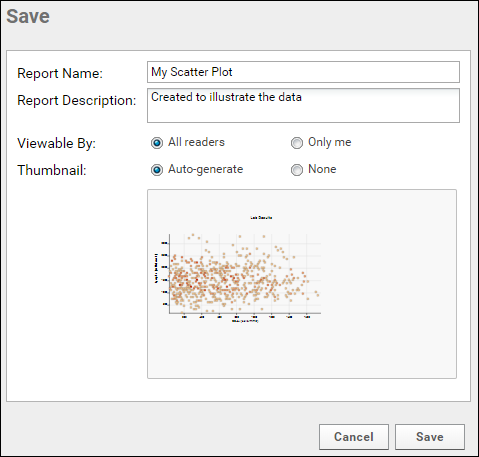
- When your plot is finished, click Save.
- Name the plot, enter a description (optional), and choose whether to make it viewable by others. You will also see the default thumbnail which has been auto-generated, and can choose whether to use it. As with other charts, you can later attach a custom thumbnail if desired.
Export Plot
Hover over the chart to reveal export option buttons in the upper right corner:- PDF: generate a PDF file.
- PNG: create a PNG image.
- Script: pop up a window displaying the JavaScript for the chart which you can then copy and paste into a wiki. See Tutorial: Visualizations in JavaScript for a tutorial on this feature.