Test Security Settings by Impersonation |
2024-04-16 |
A site or project administrator can test security settings by impersonating a user, group, or role. Using impersonation to test security can prevent granting inadvertent access to users by first testing the access a given group or role will have and only granting to the user after such testing.A project administrator's access to impersonating is limited to the current project; a site administrator can impersonate site wide.
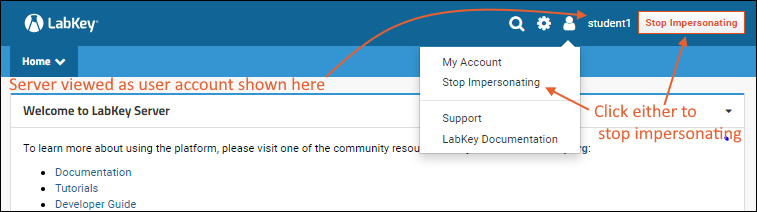
 You are now using the site as the user you selected, with only the permissions granted to that user. You can see, add, edit, as if you were that user. The username of the user you are impersonating replaces your own username in the header, and you will see a "Stop Impersonating" button.
You are now impersonating the selected group, which means you only have the permissions granted to this group. You are still logged in as you, so your display name appears in the header, and any actions you perform would be under your own userID, you are just also temporarily a member of the chosen group.
You are now impersonating the selected role(s), which means you receive only the permissions granted to the role(s). As with impersonating a group, you are still logged in as you, so your display name appears in the menu and any action you take is under your own user ID.In some cases you'll want to impersonate multiple roles simultaneously. For example, when testing specialized roles such as Specimen Requester or Assay Designer, you would typically add Reader (or another role that grants read permissions), since some specialized roles don't include read permissions themselves.When impersonating roles, the menu has an additional option: Adjust Impersonation. This allows you to reopen the role impersonation checkbox list, rather than forcing you to stop impersonating and restart to adjust the roles you are impersonating.
You are now using the site as the user you selected, with only the permissions granted to that user. You can see, add, edit, as if you were that user. The username of the user you are impersonating replaces your own username in the header, and you will see a "Stop Impersonating" button.
You are now impersonating the selected group, which means you only have the permissions granted to this group. You are still logged in as you, so your display name appears in the header, and any actions you perform would be under your own userID, you are just also temporarily a member of the chosen group.
You are now impersonating the selected role(s), which means you receive only the permissions granted to the role(s). As with impersonating a group, you are still logged in as you, so your display name appears in the menu and any action you take is under your own user ID.In some cases you'll want to impersonate multiple roles simultaneously. For example, when testing specialized roles such as Specimen Requester or Assay Designer, you would typically add Reader (or another role that grants read permissions), since some specialized roles don't include read permissions themselves.When impersonating roles, the menu has an additional option: Adjust Impersonation. This allows you to reopen the role impersonation checkbox list, rather than forcing you to stop impersonating and restart to adjust the roles you are impersonating.
- Impersonate a User
- Impersonate a Group
- Impersonate a Role
- Stop Impersonating
- Project-Level Impersonation
- Logging of Impersonations
Impersonate a User
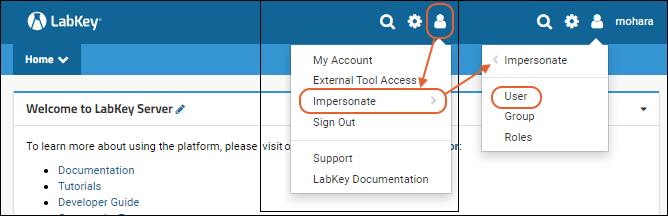
Impersonating a user is useful for testing a specific user's permissions or assisting a user having trouble on the site.- Select (User) > Impersonate > User. Note that the Impersonate option opens a sub menu listing the options.

- Select a user from the dropdown and click Impersonate
Impersonate a Group
Impersonating a security group is useful for testing the permissions granted to that group.- Select (User) > Impersonate > Group
- Select a group from the dropdown and click Impersonate
Is it Possible to Impersonate the "Guests" Group?
The "Guests" group (those users who are not logged into the server) does not appear in the dropdown for impersonating a group. This means you cannot directly impersonate a non-logged in user. But you can see the server through a Guest's eyes by logging out of the server yourself. When you log out of the server, you are seeing what the Guests will see. When comparing the experience of logged-in (Users) versus non-logged-in (Guest) users, you can open two different browsers, such as Chrome and Firefox: login in one, but remain logged out in the other.Impersonate Roles
Impersonating security roles is useful for testing how the system responds to those roles. This is typically used when developing or testing new features, or by administrators who are curious about how features behave for different levels. Note that role impersonation grants the role(s) site-wide, so can easily produce different results than impersonating a specific user with that role in one folder or project.- Select (User) > Impersonate > Roles
- Select one or more roles in the list box and click Impersonate